August 1, 2024
Enriching Transactions Beyond MCC codes

4 minutes
[lmt-post-modified-info]
MCC codes (Merchant Category Codes) is four-digit identifier assigned by credit card issuers to categorise merchants based on where you make a purchase. These codes play a vital role in various financial processes, including credit card rewards programs. However, while MCC codes offer valuable insights for transaction data enrichment, they also have limitations that need to be considered.
The Benefits of MCC Codes
- Universally Understood: Established through ISO standards1, MCCs are widely recognised by financial institutions across the globe.
- Baseline Categorisation: While not perfect, MCCs can often categorise transactions into relevant groups (e.g., groceries, clothing) over 50% of the time.
- Enhanced Data: MCC codes, when combined with other tools, can improve the accuracy of merchant data, including business names and logos.
- Fraud Detection: MCC codes can flag suspicious transactions that deviate from a cardholder’s usual spending patterns, such as unexpected travel expenses.
As banks create merchant identification systems, they must consider both the benefits and limitations of Merchant Category Codes for transaction data.
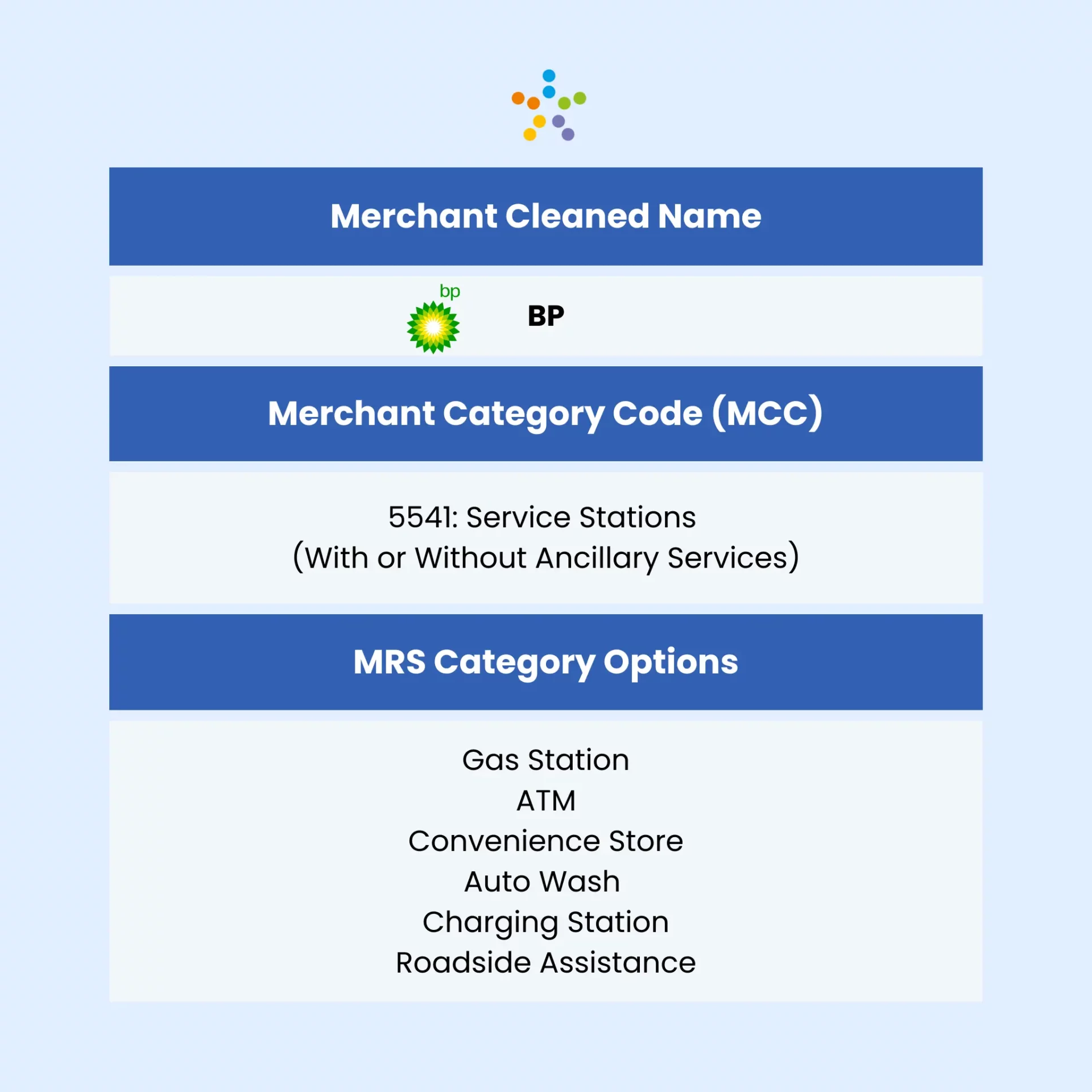
The Limitations of MCC codes
- Accuracy and Specificity Issues: MCC codes often contain outdated or inaccurate information, leading to mis-categorisation. They also lack detail, as they do not specify which department within a department store the purchase was made from.
- Geographic Limitations: Some MCC codes are only applicable in specific countries, limiting their usefulness for global transactions.
- Overly General Codes: MCC codes like 7299 for “Other Services–Not Elsewhere Classified” and 8999 for “Professional Services–Not Elsewhere Classified” are too broad. This lack of specificity undermines their ability to provide precise categorisation.
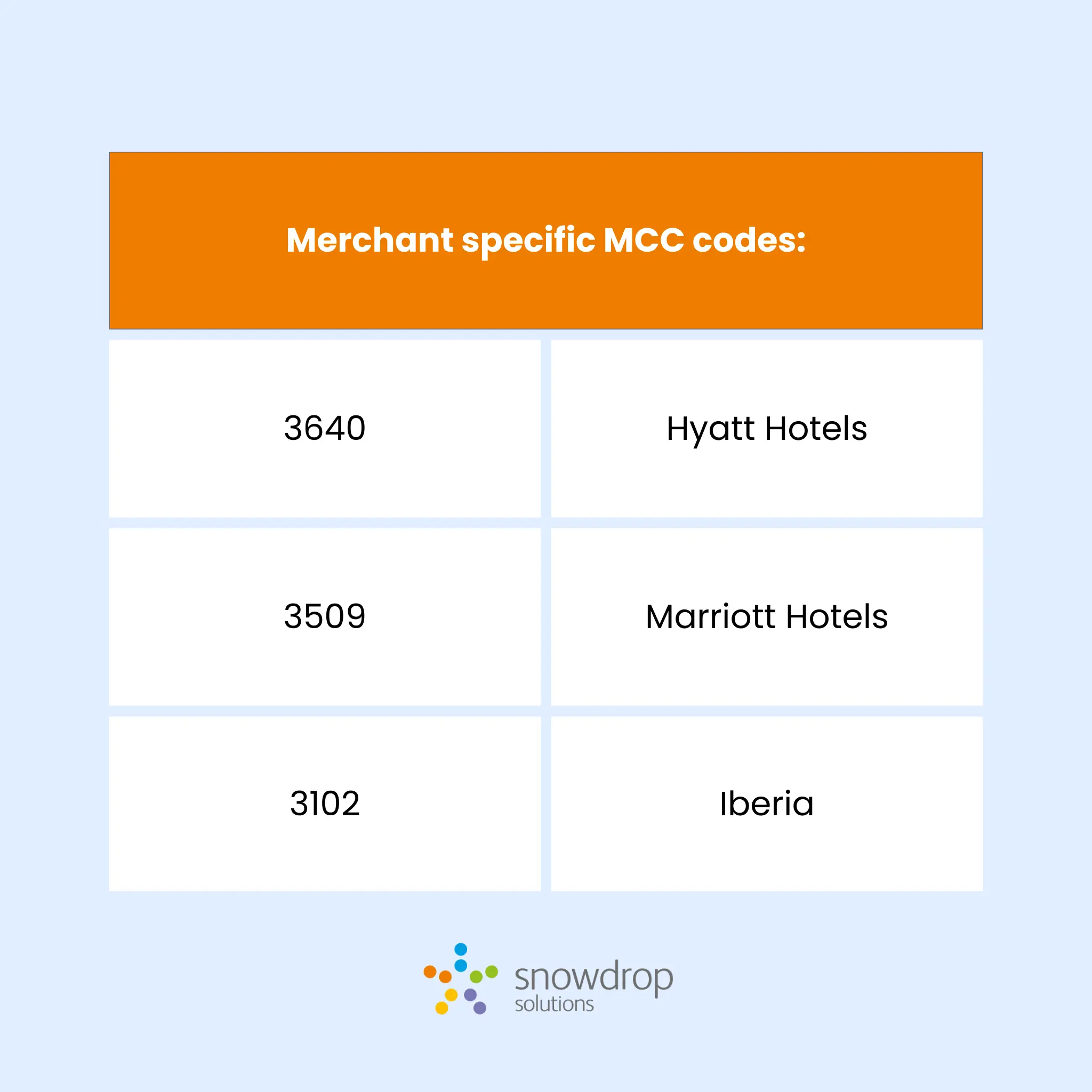
Despite these limitations, MCC codes can be useful in validating merchant data. For example, if a transaction data enrichment system accurately identifies a merchant’s name, logo, and location, validating the MCC boosts confidence in the match. Thus, MCC codes are more effective at the end of the evaluation process rather than at the beginning.
Consider Marks & Spencer, which operates across various departments like retail clothing, food, and groceries. An accurate merchant match enhances customer clarity and reduces operational costs for banks. Here, the Merchant Category Code supports the match’s confidence but is not solely reliable.
Beyond MCC codes: Enrichment Through Advanced MRS API
While Merchant Category Code provides a basic layer of information, advanced technologies can significantly improve merchant data accuracy. Our solution, the Merchant Reconciliation System (MRS), enriches raw transaction data to display clean merchant names and logos. It also provides accurate categories and precise locations on Google Maps, achieving over 80% accuracy in merchant identification.
Small pharmacies in some countries may be unidentifiable to consumers due to their unique logos that lack recognition. In such cases, the generalised category returned by the merchant category code clearly indicates a pharmacy. The enrichment algorithm then attaches a green pharmacy icon, which consumers universally recognise as representing a pharmacy. This method maintains a quality customer experience and thereby enhances the bank’s standing. This methodology not only covers pharmacies but can include tobacco shops, parking and a myriad other merchant classifications.
Conclusion
The financial services industry values MCC codes, but using them alongside advanced technologies ensures optimal accuracy and improves the customer experience. By integrating advanced transaction enrichment technology, financial institutions can offer their customers a more accurate and insightful view of their financial life. This not only benefits banks but also empowers users to make informed financial decisions.
Head of Digital Marketing
Fintech-focused digital marketer with a passion for travel, hiking, and history. Leading digital strategy and social media for a tech company. Always exploring the latest industry trends.