February 24, 2025
What is Transaction Categorization?

7 minutes
Transaction categorization is the process of organising financial transactions into specific groups based on their type. This helps banks, payment processors, and fintech companies understand users’ spending habits, manage budgets, and track financial activity more efficiently.
For example, when a customer makes a purchase using their bank card, the transaction can be classified into categories such as Groceries, Utilities, Entertainment, or Transportation. This classification helps financial institutions provide better insights and services to their users.
How Does Transaction Categorization Work?
Transaction categorization relies on several methods to classify purchases accurately. One of the main approaches involves MCC codes (Merchant Category Codes) and merchant data. MCC codes are four-digit numbers assigned to merchants by credit card networks to indicate their business type, helping banks and payment processors categorise transactions automatically.
Advanced financial tools also leverage artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning to analyse past transactions and predict the correct category for new ones, by recognising spending patterns, identifying merchant details, and learning from user corrections over time.
When combined with transaction data enrichment, AI-powered categorisation becomes even more precise. Enrichment solutions enhance raw transaction data by adding merchant names, logos, locations, and refined industry classifications – eliminating ambiguity caused by vague or inconsistent descriptors. This additional context allows AI models to cross-reference multiple data points, ensuring transactions are correctly classified even when MCC codes are broad or inaccurate.
Additionally, some banking apps allow users to manually categorise transactions when the system makes a mistake or customisation is needed. Many financial institutions also implement predefined rules and algorithms to automatically assign transactions to specific categories based on common spending patterns.
Why MCC codes do not help with accurate categorisation
It’s important to note that banks and financial institutions can’t depend solely on MCC codes (Merchant Category Codes) for transaction categorization due to several key limitations:
1. Broad and Generic Categories
- MCC codes provide a general classification of merchants based on the type of business they conduct (e.g., restaurants, retail). However, these categories are often too broad to accurately reflect a consumer’s spending behavior. For example, the “restaurant” MCC could include both fast-food chains and fine-dining establishments, making it difficult to understand the customer’s true preferences or spending patterns.
- Example: A purchase at McDonald’s and a meal at a five-star restaurant would both fall under the “Dining” category, but they represent very different consumer behaviours. Also, MCC descriptions can be very vague. MCC 5999 is “Miscellaneous and Specialty Retail Stores” or 7399 is “Business Services Not Elsewhere Classified”
2. Inaccuracies in Merchant Classification
- MCC codes are assigned by payment networks like Visa and Mastercard based on a merchant’s primary business. However, these codes don’t always reflect the actual products or services a merchant offers. Merchants may offer a variety of services that don’t fit perfectly into their assigned MCC code.
- Example: A merchant that primarily sells electronics may also provide repair services, but the MCC code may classify it under “Electronics” when a significant portion of the sales could be from services.
3. Limited Scope for Complex Transactions
- Many transactions, especially those in the digital age, may involve multiple categories of products or services, making them hard to classify using a single MCC code. Digital subscriptions, bundled services, or online marketplaces (like Amazon) don’t fit neatly into traditional MCC classifications.
- Example: A single transaction on an online marketplace like Amazon might involve the purchase of books, clothing, and electronics, but the MCC code may only categorise it as “Retail,” not capturing the variety of items purchased.
4. Changing Business Models and Merchant Types
- As businesses evolve and new business models emerge, traditional MCC codes can struggle to keep up. Companies that operate across various sectors or have multiple revenue streams may not fit into an existing MCC category.
- Example: A subscription-based service offering fitness classes, health products, and wellness content could be difficult to classify accurately using just MCC codes, as it spans across several categories.
5. Geographical and Contextual Variations
- The same business in different regions might operate under different MCC codes depending on local regulations or classification standards. This inconsistency can lead to inaccurate categorizations if a bank only relies on MCC codes without considering regional variations.
- Example: A hotel in one country may fall under a “Lodging” MCC code, while in another, it may be classified differently, complicating transaction analysis for users traveling abroad.
6. Inability to Reflect Customer Intent or Behavior
- MCC codes do not reflect the specific intent or behavior behind a transaction. For instance, a customer may use a card at a merchant categorised as a “grocery store,” but they might only be buying non-essential items like snacks or luxury food items, which could affect their budgeting or financial planning.
- Example: A person buying organic food at a local store might want to track spending under “Healthy Living” rather than “Groceries,” but MCC codes will categorise it in a generic way.
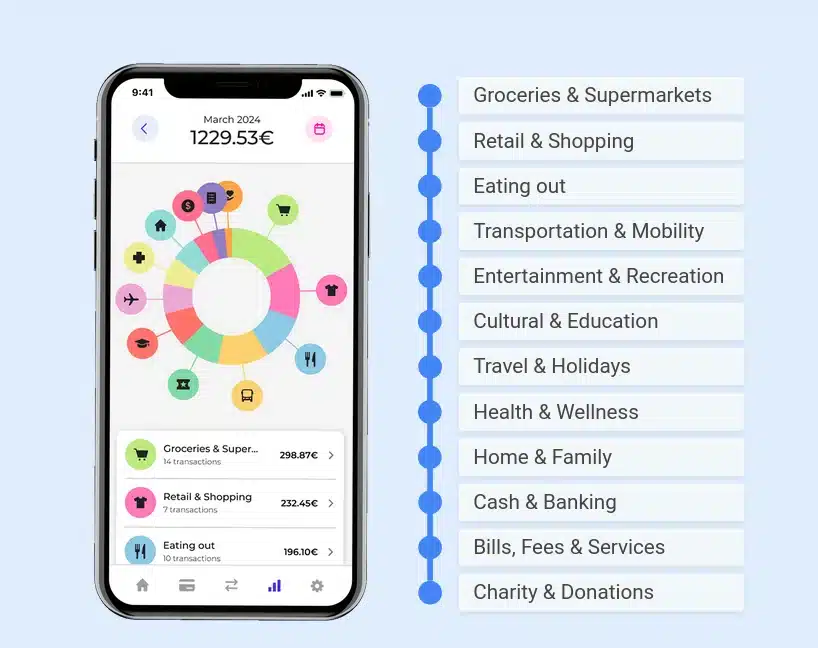
How Transaction Categorization Work in the Mobile App
- Users can view their categorised transactions in a simple, visual format, such as pie charts or spending summaries.
- Some apps allow users to customise categories or reassign transactions for better accuracy.
- AI-powered apps learn from user behavior and refine categorization over time.
- Budgeting tools help users set spending limits based on different categories.
- Alerts and insights notify users about unusual spending or opportunities to save money.

Why is Transaction Categorization Important for Banks and Fintech Companies?
Revenue Opportunities: By understanding how customers spend across various categories, financial institutions can offer personalised products like savings accounts, credit cards, or loans tailored to their habits. This customisation makes these products more appealing, increasing the likelihood of adoption and generating more revenue from product offerings.
Regulatory Compliance: In some jurisdictions, providing clear and accurate data to customers is required by law. Categorization helps ensure that banks comply with these requirements, especially in terms of transparency and disclosure.
Improved Customer Retention: Offering valuable features based on categorised transaction data, such as detailed spending reports or budgeting tips, enhances the customer experience and leads to higher retention rates. Retained customers are more likely to continue using services and purchase additional products, thus boosting overall revenue.
Targeted Marketing and Cross-Selling: Categorised transaction data helps institutions run more effective marketing campaigns, targeting customers with products that align with their spending patterns, such as offering rewards or loyalty programs based on their transaction history. This leads to increased sales and higher customer lifetime value.
Fraud Detection: Categorization can aid in spotting unusual or suspicious transactions. If a transaction doesn’t fit within an expected category, it may trigger alerts, helping banks detect and prevent fraud more effectively.
Transaction Categorization Integration into Banking Systems
- API-Based Solutions – Many financial APIs offer transaction categorization services that can be integrated into banking and fintech platforms.
- AI & Machine Learning Models – Custom AI models can be trained on transaction data to improve categorization accuracy and provide advanced financial insights.
- Cloud-Based Analytics – Cloud solutions enable real-time categorization and analysis of vast amounts of transaction data.
- Collaboration with Data Providers – Partnering with transaction data enrichment providers can enhance accuracy and add valuable metadata to transactions.
Conclusion
Transaction categorization is a powerful tool that simplifies financial management for banks, payment processors, and fintech companies. By organising financial activity into clear categories, financial institutions can gain deeper insights, enhance customer experience, and improve fraud detection and risk management. With the advancements in AI and machine learning, transaction categorization continues to evolve, making financial tracking more accurate, efficient, and valuable for the financial industry.
Head of Digital Marketing
Fintech-focused digital marketer with a passion for travel, hiking, and history. Leading digital strategy and social media for a tech company. Always exploring the latest industry trends.